Know the Rights and Duties of Bailor and Bailee in India

Bailment is an act wherein one individual temporarily gives the possession of their property to another individual. The person who gives possession is the bailor. The person who takes possession is the bailee. The bailee has the responsibility to safekeep the property and return it after the time period agreed upon.
If the bailor fails to fulfill their duty, the bailor has the right to sue them for damages. In this blog post, we will discuss the rights and duties of bailor and bailee.
Who is Bailor?
Bailor is an individual or a party that gives property to someone else to use or take care of temporarily. The bailee must return the property to the bailor once the purpose is accomplished.
For example: If A lends a book to B, then A is the bailor. B must return the book to A once they have read the book.
Rights and Duties of Bailor
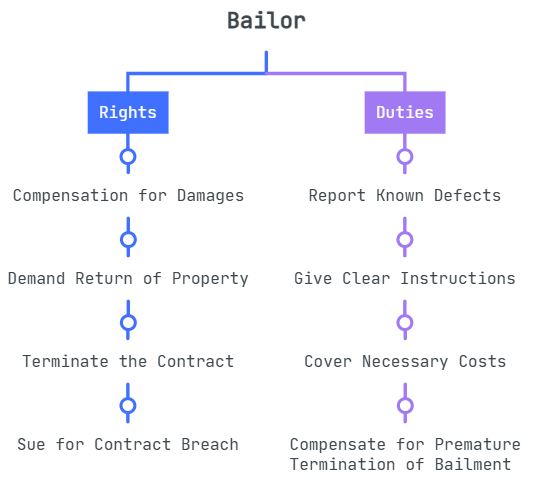
Rights of Bailor
The rights of a bailor include:
- Right to Compensation for Damages: During the bailment period, the bailor has the right to seek compensation for damages or loss suffered due to the goods.
- Right to Demand Return of Property: Once the purpose of bailment is accomplished, the property must be returned to the bailor.
- Right to Terminate the Contract: The bailment can be terminated by the bailor any time even if the purpose of bailment has not been fulfilled. However, the bailee must be compensated in a fair and reasonable manner.
- Right to Sue for Contract Breach: If the bailee breaches the contract, the bailor can sue them and seek appropriate legal remedies, such as damages for any loss suffered.
- Right to Terminate Bailment due to Inconsistency with Conditions: The bailor may terminate the contract if the bailee violates its terms.
Duties of Bailor
Apart from having rights, the bailor also has certain duties such as:
- Duty to Report Known Defects: It is the bailor’s duty to notify the bailee of defects or risks related to the goods. This obligation occurs when the bailor knows of any concealed flaws that could endanger the bailee or other parties.
- Duty to Give Clear Instructions: The bailor has a duty to provide clear instructions to the bailee regarding the property’s intended use, the purpose of the bailment, and any special terms or restrictions related to the bailment.
- Duty to Cover Necessary Costs: The bailor is responsible for covering the costs that the bailee will incur throughout the ordinary course of the bailment. This covers costs including storage fees and appropriate costs to keep the product/property safe during the bailment time.
- Duty to Compensate for Premature Termination of Bailment: If the bailor terminates the bailment before the purpose is accomplished, they have the duty to compensate the bailee for losses incurred due to bailment’s premature termination.
Who is Bailee?
A bailee is the opposite of a bailor. A bailee is an individual who receives property from the bailor for a specific purpose. When the purpose is completed, the bailee is required to return the property.
For example: If A gives their clothes to B for dry cleaning, B is the bailee. After dry cleaning, B must return the clothes to A.
Rights and Duties of Bailee
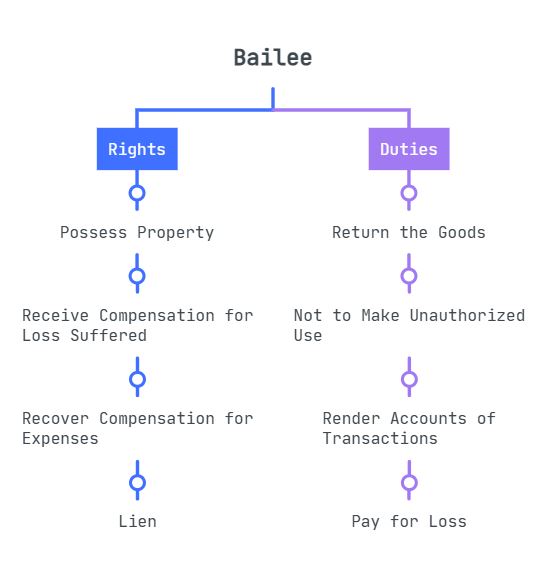
Rights of Bailee
The rights of a bailee are the following:
- Right to Possess Property: The bailee has the right to possess property as part of the bailment. However, the property must only be used for specific purposes for which they were delivered.
- Right to Receive Compensation for Loss Suffered: If the bailor fails to disclose about risks associated with the property, and the bailee suffers loss because of it, the bailee can ask for compensation. For instance, if the bailor lends a dog that they know is ferocious but still doesn’t disclose it, the bailor is held liable for injuries sustained by the bailee.
- Right to Lien: This right allows the bailee to retain possession of goods until the bailor pays charges due to the bailee for services provided in respect of the property.
- Right to Recover Compensation for Expenses: Any costs incurred within the ordinary course of bailment must be reimbursed to the bailee. For example, the bailor is required to reimburse the bailee for any costs incurred related to the maintenance of property.
Duties of Bailee
The bailee must fulfill the following duties:
- Duty to Return the Goods: Once the purpose of bailment is fulfilled, the bailee must return the goods to the bailor.
- Duty Not to Make Unauthorized Use: The goods covered by the bailment cannot be used in any way that the bailee is not permitted to use. The goods must only be used for the specified purpose for which they were entrusted.
- Duty to Pay for Loss: The bailee is responsible for paying the bailor for any loss or damage to the goods that result from his or her carelessness. The bailee must take the required precautions and conduct due diligence to avoid any loss or damage to the goods.
- Duty to Render Accounts of Transactions: The bailee must give accurate reports of all transactions related to the bailment if the bailor asks. The bailee is required to keep accurate records and be open and honest in all transactions pertaining to the bailment.
Difference between Bailor and Bailee
The following table represents the difference between bailor and bailee:
| Parameters | Bailor | Bailee |
| Definition | Bailor is an individual who gives goods to the bailee. | Bailee is an individual who receives goods from the bailor. |
| Ownership | Bailor owns the property. | Bailee does not own the property and only takes care of it until the purpose is accomplished. |
| Role | Bailer entrusts possession to the bailor. | Bailee holds the possession given by the bailor. |
| Relationship | Creates the terms and conditions of the bailment. | Agrees to the terms and conditions of the bailment. |
| Example | Lender of a book, owner of a car rental business and owner of a rental clothes business. | Dry cleaner, car mechanic and jewelry repair shop. |
Conclusion
The bailor and bailee are the two parties involved in a bailment. A bailment is a legal agreement whereby one party (bailor) temporarily transfers possession of their property to another party (bailee). Once the purpose of bailment is accomplished, the property must be returned by the bailee to the bailor. You may also like to read about
Liked this blog post? Don’t forget to read about Transfer Of Property Act 1882 .
Categories: Legal
Tags: